

They take the form of rings or macrocycles, and due to the absence of chain ends, all repeating units are physically and chemically equivalent. Amongst these attributes, the shape of the carrier has been identified as one of the key factors 2, 3.Ĭyclic polymers may be an innovative choice for this purpose due to their unique properties and cyclic structure. The physical and chemical properties of the polymeric carriers are critical to the therapy’s success. Polymers usually show longer circulation time and the potential for tissue targeting 1. Synthetic polymers are intriguing drug delivery candidates. The results were presented and thoroughly discussed. Polymers were characterized by 1HNMR, FTIR, DSC, TLC, GPC, and viscometry tests. In cyclic reactions, the addition of DMF as a co-solvent resulted in the formation of a polymer with a high viscosity average molecular weight (M v) and a high degree of cyclization (100%), whereas the CO 2/water emulsion resulted in the formation of a polymer with a lower M v and increased porosity. Furthermore, the effect of cyclization reaction types on the properties of cyclic polymers was investigated. Additionally, a lower pressure reduced the solubility of materials (particularly terminator) in SC-CO 2 and resulted in a chain with a higher molecular weight 9326 (gr/mol), leading to a lower conversion. The maximum yield was 64% at 23 MPa, and the chain molecular weight (M w) was 4368 (gr/mol). The effects of pressure and time on the morphology, molecular weight, and yield of a difunctionalized chain were investigated, where a higher pressure led to a higher yield. This reaction was also conducted in emulsion of SC-CO 2 in water. The cyclization reaction occurred in a homogeneous phase in the SC-CO 2 solvent, with dimethylformamide (DMF) serving as a co-solvent for dissolving the linear precursor.
KBR MOLAR MASS FREE
This was accomplished by applying free radical polymerization and nitroxide compounds to produce low molecular weight precursors in the SC-CO 2 solvent. Please let us know how we can improve this web app.In this study, cyclic poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) (cPNIPAAM) was synthesized in supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO 2) using emulsion and homogeneous reactions for the first time. Related: Molecular weights of amino acids Weights of atoms and isotopes are from NIST article. Molar mass ( molar weight) is the mass of one mole of a substance and is expressed in g/mol.(1 u is equal to 1/12 the mass of one atom of carbon-12) Molecular mass ( molecular weight) is the mass of one molecule of a substance and is expressed in the unified atomic mass units (u).
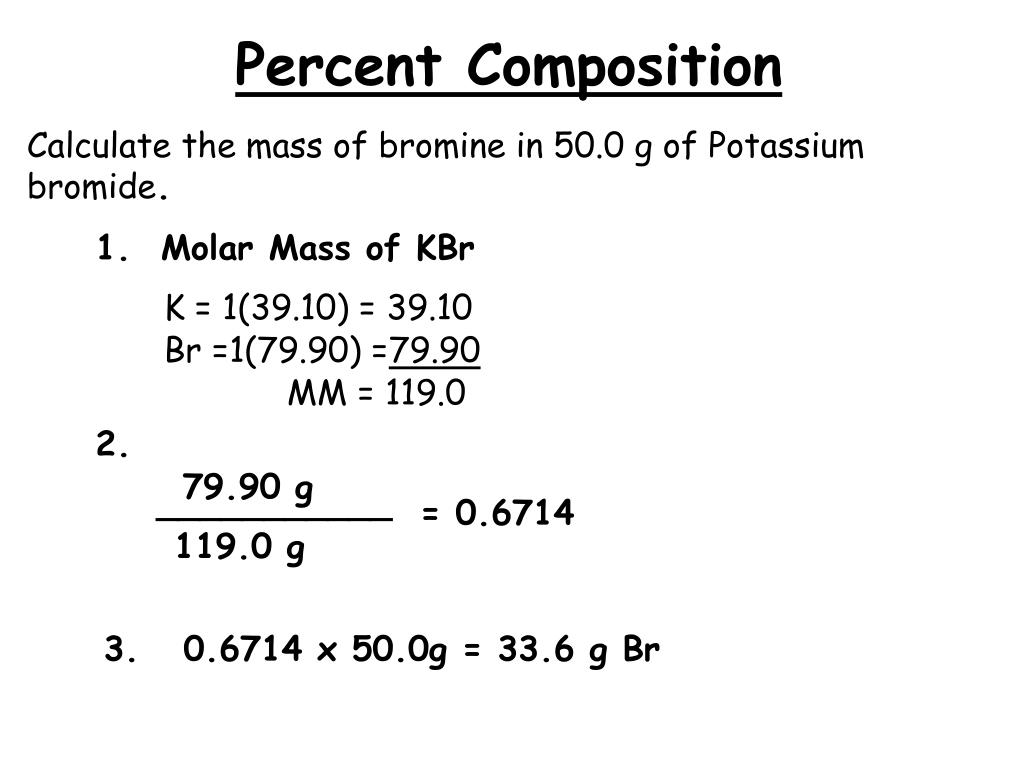

To calculate molecular weight of a chemical compound enter it's formula, specify its isotope mass number after each element in square brackets.Įxamples of molecular weight computations:ĭefinitions of molecular mass, molecular weight, molar mass and molar weight Molar mass calculator also displays common compound name, Hill formula, elemental composition, mass percent composition, atomic percent compositions and allows to convert from weight to number of moles and vice versa.Ĭomputing molecular weight (molecular mass)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
